
Comparison of complication rates of retropubic and transobturator approaches in application of tension-free vaginal tape
Article authors


Clinic of Urology MSMSU
Hypothesis / aims of study
An objective of the study was comparison of complication rate and safety of tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) applied via retropubic or transobturator approaches in females suffering stress urinary incontinence (SUI). In order to gain this objective other factors influencing cure rate shall be minimized, such as surgeons' experience, tape characteristics or recurrent incontinence SUI.
Study design, materials and methods
460 patients with SUI underwent surgical treatment in our Urology Department. Patients with detrusor overactivity, recurrent incontinence and those cases when the tape other than macropore polypropylene was used were ruled out from the study. Same experienced urologists did the surgery in both groups. Only 310 patients from 460 met these inclusion criteria. In accordance with that 202 patients formed Group 1 when retropubic TVT was utilized. Group 2 included 108 females treated with TVT via transobturator approach. Mean age in group 1 was 54,7±11,9 yrs. (29-76), and 53,6±12,5 yrs. (35-79) for Group 2 (p=0,446). There were no significant difference between the Group 1 and 2 in matter of menopause (66,6% vs. 59,3%; p=0,54), BMI (24±3,2 vs.25,2±4,3; p=0,058) and parity (2,3±0,9 vs. 2,0±1,9; p=0,6) accordingly. Mean postoperative follow-up ranged 4±4,3 yrs. for Group 1 and 3,1 ±3,14 yrs. for Group 2 patients (p=0,061)
Results
According to our results, the cure rate in Group 1 (retropubic TVT - 93,53%) and Group 2 (transobturator TVT - 92,95%) has no significant difference (p=0,58). Comparison of complication rate showed no statistical significance as well. Four patients in each group failed treatment (1,98% in TVT group and 3,70% after TVT-O; p=0,36). One patient in Group 1 developed bladder perforation (0,49%). No bladder injury was found in Group 2. De novo urgency appeared in 4,46% and 3,70% cases in Group 1 and 2 (p= 0,73). Hematomas requiring intervention were noticed in 2,97% cases in Group 1 and 0,93% cases in Group 2 (p= 0,24). These data are presented in histogram 1.
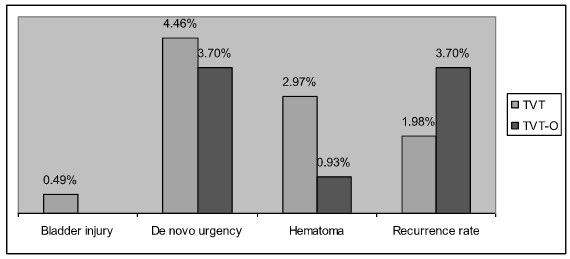
Histogram 1
Interpretation of results
We have ruled out additional affecting factors like tape bio-physical characteristics, surgeons’ experience and cases with recurrent SUI for adequate comparison of retropubic and transobrurator TVT. The study results revealed no difference in efficacy and safety when comparing retropubic and transobturator approaches of TVT placement. There is no significant difference in complication rate for both methods. Retropubic and transobturator TVT procedures are equally effective and safe in treatment of female SUI. Surgical approach of TVT application does not affect cure rate.
Concluding message
We have ruled out additional affecting factors like tape bio-physical characteristics, surgeons’ experience and cases with recurrent SUI for adequate comparison of retropubic and transobrurator TVT. The study results revealed no difference in efficacy and safety when comparing retropubic and transobturator approaches of TVT placement. There is no significant difference in complication rate for both methods. Retropubic and transobturator TVT procedures are equally effective and safe in treatment of female SUI. Surgical approach of TVT application does not affect complication rate of these procedures.
| Specify source of funding or grant | 460 |
| Is this a clinical trial? | No |
| What were the subjects in the study? | HUMAN |
| Was this study approved by an ethics committee? | No |
| This study did not require eithics committee approval because | It is retrospective comparative study of our experience in treatment of female stress urinary incontinence |
| This study did not require eithics committee approval because | Yes |
| Was informed consent obtained from the patients? | Yes |






